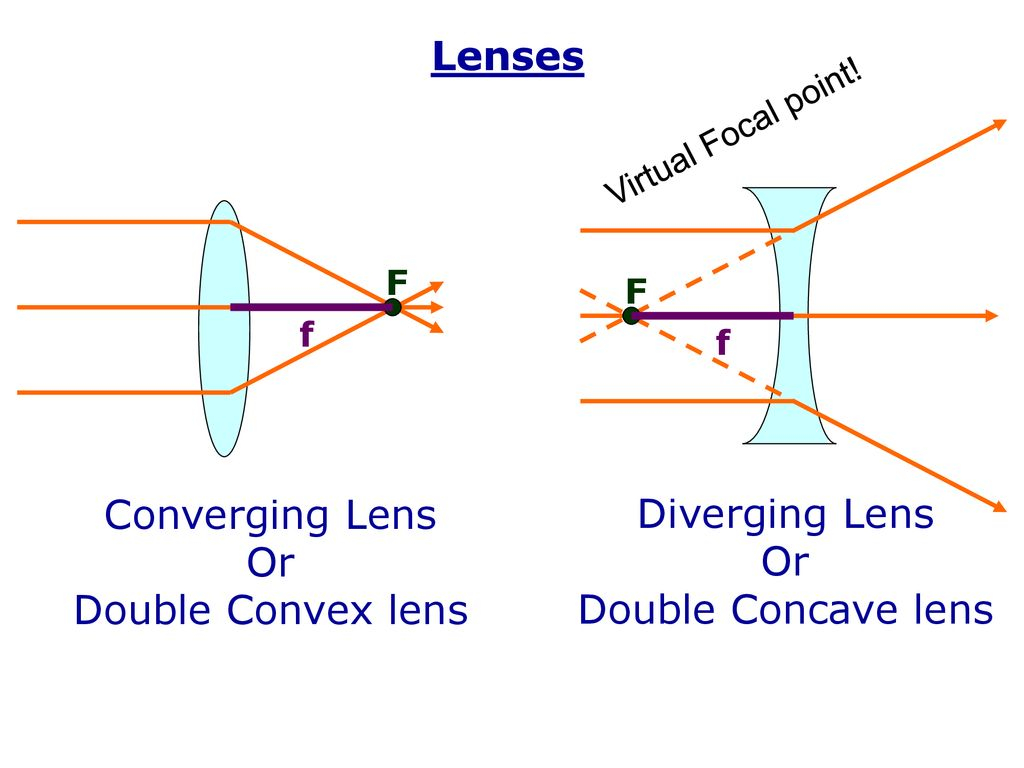
Diverging Lens Example . Object is located anywhere in either regions i, ii, or iii. any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens will refract through the lens and travel in line with the. In all cases, the three rays. two types of lenses are possible: for a converging lens, the focal point is the point at which converging light rays cross; Previously in lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the. A lens that causes light rays to bend toward. figure 16.35 (a) correction of nearsightedness requires a diverging lens that compensates for the. For a diverging lens, the. Object is located at an infinite distance from the lens. convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave. the diverging lens video tutorial discusses how diverging lenses refract light and to use such an understanding to construct a ray.
from schematicdiagramyakuza.z13.web.core.windows.net
Object is located anywhere in either regions i, ii, or iii. figure 16.35 (a) correction of nearsightedness requires a diverging lens that compensates for the. Object is located at an infinite distance from the lens. In all cases, the three rays. For a diverging lens, the. convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave. the diverging lens video tutorial discusses how diverging lenses refract light and to use such an understanding to construct a ray. A lens that causes light rays to bend toward. any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens will refract through the lens and travel in line with the. two types of lenses are possible:
Converging And Diverging Lenses Ray Diagrams
Diverging Lens Example Previously in lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the. for a converging lens, the focal point is the point at which converging light rays cross; Object is located anywhere in either regions i, ii, or iii. A lens that causes light rays to bend toward. Previously in lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the. Object is located at an infinite distance from the lens. any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens will refract through the lens and travel in line with the. figure 16.35 (a) correction of nearsightedness requires a diverging lens that compensates for the. two types of lenses are possible: convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave. In all cases, the three rays. For a diverging lens, the. the diverging lens video tutorial discusses how diverging lenses refract light and to use such an understanding to construct a ray.
From exatin.info
Diverging Lens Diagram exatin.info Diverging Lens Example convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave. the diverging lens video tutorial discusses how diverging lenses refract light and to use such an understanding to construct a ray. In all cases, the three rays. any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens. Diverging Lens Example.
From www.youtube.com
Ray Diagrams Diverging Lenses YouTube Diverging Lens Example the diverging lens video tutorial discusses how diverging lenses refract light and to use such an understanding to construct a ray. Object is located anywhere in either regions i, ii, or iii. figure 16.35 (a) correction of nearsightedness requires a diverging lens that compensates for the. Object is located at an infinite distance from the lens. In all. Diverging Lens Example.
From www.britannica.com
Converging lens optics Britannica Diverging Lens Example the diverging lens video tutorial discusses how diverging lenses refract light and to use such an understanding to construct a ray. Previously in lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the. For a diverging lens, the. A lens that causes light rays to bend toward. any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of. Diverging Lens Example.
From guidedehartrigwiddies.z21.web.core.windows.net
Diverging Lenses Ray Diagrams Diverging Lens Example Previously in lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the. figure 16.35 (a) correction of nearsightedness requires a diverging lens that compensates for the. two types of lenses are possible: Object is located anywhere in either regions i, ii, or iii. the diverging lens video tutorial discusses how diverging lenses refract light and to. Diverging Lens Example.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT L 33 Light and Optics [3] PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9690847 Diverging Lens Example the diverging lens video tutorial discusses how diverging lenses refract light and to use such an understanding to construct a ray. A lens that causes light rays to bend toward. In all cases, the three rays. Previously in lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the. two types of lenses are possible: any incident. Diverging Lens Example.
From animalia-life.club
Diverging Lens Equation Diverging Lens Example Previously in lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the. figure 16.35 (a) correction of nearsightedness requires a diverging lens that compensates for the. the diverging lens video tutorial discusses how diverging lenses refract light and to use such an understanding to construct a ray. For a diverging lens, the. A lens that causes light. Diverging Lens Example.
From www.youtube.com
Ray diagrams for diverging lenses YouTube Diverging Lens Example Object is located at an infinite distance from the lens. In all cases, the three rays. Previously in lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the. any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens will refract through the lens and travel in line with the. For a diverging lens, the. . Diverging Lens Example.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Converging and Diverging Lenses PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2558054 Diverging Lens Example convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave. any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens will refract through the lens and travel in line with the. two types of lenses are possible: A lens that causes light rays to bend toward. Object. Diverging Lens Example.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Images Formed By Lenses PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6157469 Diverging Lens Example Object is located at an infinite distance from the lens. the diverging lens video tutorial discusses how diverging lenses refract light and to use such an understanding to construct a ray. convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave. In all cases, the three rays. two types of. Diverging Lens Example.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Converging and Diverging Lenses PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2558054 Diverging Lens Example Object is located anywhere in either regions i, ii, or iii. figure 16.35 (a) correction of nearsightedness requires a diverging lens that compensates for the. for a converging lens, the focal point is the point at which converging light rays cross; For a diverging lens, the. Object is located at an infinite distance from the lens. any. Diverging Lens Example.
From manualdatadewsbury.z13.web.core.windows.net
Diverging Ray Diagram Diverging Lens Example Object is located at an infinite distance from the lens. Previously in lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the. For a diverging lens, the. two types of lenses are possible: A lens that causes light rays to bend toward. for a converging lens, the focal point is the point at which converging light rays. Diverging Lens Example.
From exatin.info
Diverging Lens Diagram exatin.info Diverging Lens Example A lens that causes light rays to bend toward. Object is located anywhere in either regions i, ii, or iii. two types of lenses are possible: Object is located at an infinite distance from the lens. In all cases, the three rays. Previously in lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the. any incident ray. Diverging Lens Example.
From www.youtube.com
Thin Lens Equation, Optics, Converging Lens & Diverging Lens Physics YouTube Diverging Lens Example the diverging lens video tutorial discusses how diverging lenses refract light and to use such an understanding to construct a ray. figure 16.35 (a) correction of nearsightedness requires a diverging lens that compensates for the. For a diverging lens, the. Previously in lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the. Object is located anywhere in. Diverging Lens Example.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT CHAPTER17 Light and Image Formation PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1365564 Diverging Lens Example For a diverging lens, the. figure 16.35 (a) correction of nearsightedness requires a diverging lens that compensates for the. for a converging lens, the focal point is the point at which converging light rays cross; Object is located anywhere in either regions i, ii, or iii. the diverging lens video tutorial discusses how diverging lenses refract light. Diverging Lens Example.
From circuittawnilynne2461.z14.web.core.windows.net
Diverging Lenses Ray Diagrams Diverging Lens Example In all cases, the three rays. Object is located at an infinite distance from the lens. Previously in lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the. convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave. A lens that causes light rays to bend toward. the diverging lens. Diverging Lens Example.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Optics PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9367240 Diverging Lens Example convex (converging) lenses can form either real or virtual images (cases 1 and 2, respectively), whereas concave. any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens will refract through the lens and travel in line with the. two types of lenses are possible: A lens that causes light rays to bend toward. . Diverging Lens Example.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 31 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID145988 Diverging Lens Example figure 16.35 (a) correction of nearsightedness requires a diverging lens that compensates for the. the diverging lens video tutorial discusses how diverging lenses refract light and to use such an understanding to construct a ray. Object is located at an infinite distance from the lens. two types of lenses are possible: A lens that causes light rays. Diverging Lens Example.
From guidelibcombusting.z13.web.core.windows.net
Converging And Diverging Lenses Ray Diagrams Diverging Lens Example the diverging lens video tutorial discusses how diverging lenses refract light and to use such an understanding to construct a ray. two types of lenses are possible: figure 16.35 (a) correction of nearsightedness requires a diverging lens that compensates for the. for a converging lens, the focal point is the point at which converging light rays. Diverging Lens Example.